Brands know they need artificial intelligence, and their programmatic advertising partners know they would have a hard time working without it.
But as data volumes grow exponentially and AI speeds up its ability to process this data through machine learning, a glaring issue for marketers has been a lack of clarity in understanding how the AI is working. Marketers want to see where their money is being spent and why. Just saying that “AI optimized it” won’t cut it.
Data visualization can play a big role in helping to distill the complexity of multiple metrics and processes into a visually appealing presentation that can be quickly understood and then delved into for further detail. Our Copilot team, which develops proprietary technology at Xaxis, has been working to make AI more accessible for a few years. I’m tasked with translating our bespoke AI models into visualizations that provide insights for agencies and brands.
A good visualization communicates the truth in data, but which truth depends on what is being communicated, and to whom. To effectively design a visualization is to know the data intimately but, more important, to understand the needs of the audience it is speaking to. The audience of the visualization must be top of mind when designing.
For example, a visualization designer should consider:
- Müssen die Daten über einen bestimmten Zeitraum dargestellt werden?
- Welche Metriken sind am wichtigsten?
- Welche Bereiche einer Visualisierung müssen "knallen"?
Aufbau einer Visualisierung, in der Praxis
Kürzlich haben wir einige neue Datenvisualisierungen eingeführt, um eine unserer algorithmischen Strategien zu erläutern, die Massen von nicht-menschlichen Entscheidungen auf eine leicht verdauliche und dennoch nicht triviale Weise zeigen.
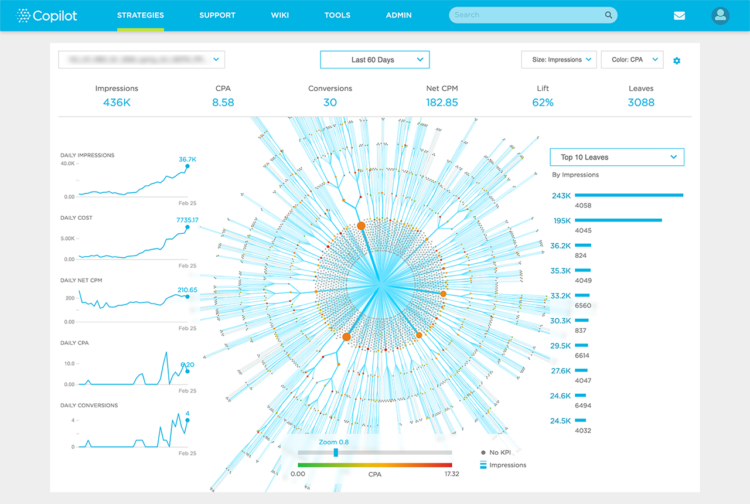
Die Grafik auf dieser Seite fasst eine Fülle komplexer Erkenntnisse auf eine Art und Weise zusammen, die ein Mensch schnell begreifen kann: wie die Cost-per-Action (CPA) der gekauften Impressionen sank, selbst als die Anzahl der Impressionen stieg und ihre Preisgestaltung (dargestellt durch CPM) relativ konstant gehalten wurde. Anhand der konzentrischen Kreise können Sie sehen, wie die KI den Prozess steuern konnte, als sich das Ad Targeting von CPAs und begrenzten KPIs entfernte, um sich schließlich auf Impressionen zu konzentrieren, die gut bepreist waren und wirksam waren.
Datenvisualisierung kann den traditionellen UX-Design-Praktiken ähnlich sein. Sowohl UX-Design als auch Datenvisualisierung beinhalten Benutzerforschung, die Modellierung von Anwendungsfällen, Interviews mit der Zielgruppe und viele Testlayouts. Das Durchlaufen dieses Prozesses zeigt dem Designer, welche Erkenntnisse das Publikum sucht und offenbart Fragen, die durch das Design beantwortet werden müssen.
Datenvisualisierung als Kunst
Despite protest from some within the data visualization community, I consider data visualization to be the art of the computer science world. The aesthetic aspect of design is an essential component of strong visualizations. Practitioners of data visualization should consider the artfulness of our work.
Being artful doesn't diminish the value of a visualization. Rather, it allows it to transcend the data and captivate the spirit. Doing so requires a deep focus on both highlighting the right data for a given audience and respecting the art of design.
Color choice, spacing, and movement should all be top of mind when working with data. Beautiful visualizations are comprised of numbers and formulas that inform shapes and colors.
There are great lengths to go to in order to further improve how we visualize the bounties that AI and machine learning can bring. A focus on both relevant data and aesthetics will ensure that this discipline will continue to bring tremendous value to marketers.